Comparative study of biogas yield from animal manure in barn and farm
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.57056/ajet.v8i1.84Keywords:
Biogas yield, Animal manure, Anaerobic digestion, Method of the pasture, Clean energyAbstract
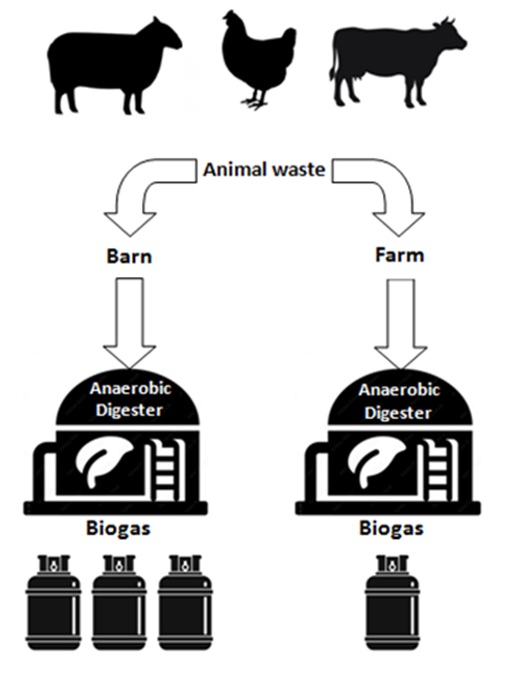
The need for energy crops and animal manures for the production of biogas is rising globally. Farmers that raise cattle may use manure as an alternative energy source. Manure is partially converted into energy in the form of biogas by an anaerobic digester. To improve the biogas yield from animal manure must be taken into consideration the quality of manure. It is clear that the difference in the method of pasture has an important impact on biogas production. The study aims to compare the amount of biogas produced from manure animals in barns (closed pastures) and animals in farms (open pastures). The study included different types of manure cows, sheep, and poultry. Experiments were performed in a 2 L plastic bottle digester in a water bath at a 37°C mesophilic range. During the 12-day hydraulic retention period, a mixture of animal dung and water was employed in a 1:1 ratio (HRT). The volumetric water replacement method was used to calculate the amount of gas produced. The results showed that the barn manure had higher biogas production than the farm manure approximately 3 times because their feed had concentrated nutritional supplements.
References
Drożyner P , Rejmer W, Starowicz P, Klasa A, Skibniewska KA. Biomass As A Renewable Source Of Energy. Technical Sciences. 2013; 16 (3): 211–220.
Adebimpe OA, Edem I E, Ayodele OL. Investigation Of The Effects Of Starting Ph, Mass And Retention Time On Biogas Production Using Poultry Droppings As Feedstock. Nigerian Journal of Technology (NIJOTECH). 2020; 39 (1): 203 – 211.
RECEBLI1 Z, SELIMLI1 S, OZKAYMAK1 M., GONC O. Biogas Production From Animal Manure. Journal of Engineering Science and Technology. 2015; 10 (6): 722 – 729.
Benali M. Utilization of Cow, Poultry and Sheep Manure for biogas Production: A Comparative Analysis, Master’s thesis, Faculty of Engineering, Omar Al-Mukhtar University, Libya, 2o2o.
Khedim Z, Benyahia B, Cherki B, Sari T, Harmand J. Effect of control parameters on biogas production during the anaerobic digestion of protein-rich substrates. Applied Mathematical Modelling. 2018; 61: 351-376.
Laskri N, Nedjah N. Comparative Study for Biogas Production from Different Wastes. International Journal of Bio-Science and Bio-Technology. 2015; 7: 39-46. https://doi.org/10.14257/ijbsbt.2015.7.4.05
Al-Hamamre Z, Al-Mater A, Sweis F. and Rawajfeh, K. Assessment of the Status and Outlook of Biomass Energy in Jordan. Energy Conversion and Management. 2014; 77: 183-192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2013.09.041
Al Jabri SJ, Sharkh MSA. Generation of Biogas from Bio-Waste in Rural Area of Palestine. International Proceedings of Chemical. Biological and Environmental Engineering (IPCBEE). 2013; 57: 57-61.
Marañón E, Castrillón L, Quiroga G, Fernández-Nava Y, Gómez L, García M. Co-Digestion of Cattle Manure with Food Waste and Sludge to Increase Biogas Production. Waste Management. 2012; 32: 1821-1825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2012.05.033
Esposito G, Frunzo L, Panico A, Pirozzi F. Enhanced Bio-Methane Production from Co-Digestion of Different Organic Wastes. Environmental Technology. 2012; 33: 2733-2740. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2012.676077
Hamed TA, Flamm H, Azraq M. Renewable Energy in the Palestinian Territories: Opportunities and Challenges. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2012; 16: 1082-1088. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2011.10.011
Al-Amin AM., Al-Shaw F. Al-Gadban S. Design, Install and Apply the Biogas Unit At the Faculty of Agriculture (Kharabo) Farm Damascus University. Journal of Damascus University for Agriculture Science.2007; 23: 390-379.
Mohammed M, Belkair A, Hamad T, Jirhiman I, Hassan R, Ahmeedah A. Improving biogas production from animal manure by batch anaerobic digestion. Alger. J. Eng. Technol. 2022, 6:79-84.
Hammad EI, Al-Agha MR. and El-Nahhal Y. Enhancing Biogas Production: Influence of Mixing Cow and Chicken Manures. Energy and Power Engineering. 2018; 10: 383-397.
Wagner AO, Lins P, Malin C, Reitschuler C , Illmer P. Impact of protein-, lipid- and cellulose-containing complex substrates on biogas production and microbial communities in batch experiments. Science of the Total Environment. 2013; 458–460: 256–266.
Hindrichsen I K,. Wettstein HR, Machmu Ller A, JORG B, Kreuzer M. Effect of the carbohydrate composition of feed-concentratates on methane emission from dairy cows and their slurry. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. 2005; 107: 329–350.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Muetaz Mohammed, Sulaiman Boghandora, Razena Hassan, Abraheem Jirhiman, Ali Ahmeedah

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.





