Improving biogas production from animal manure by batch anaerobic digestion
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.57056/ajet.v6i1.74Keywords:
Biogas, Effect pH, Photoreactor, Animal Manure, Batch DigestionAbstract
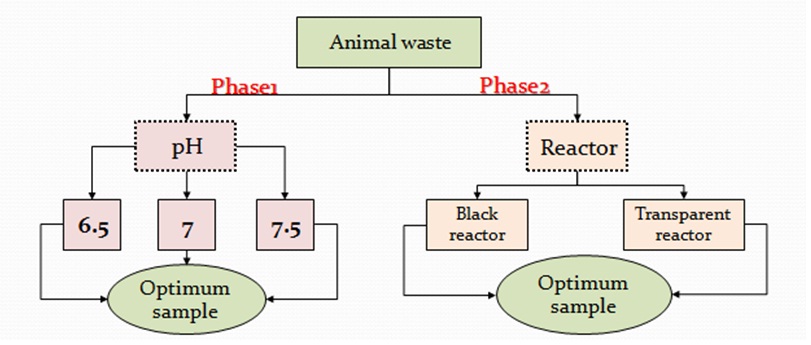
In Libya, even if the production of biogas started in the last years, still there is too much need to optimize the biogas resources. This paper examined improving cow, sheep, and poultry manure in two phases. The experiment was carried out in a 2000 mL digester put in bath water at 37 °C. The mixing ratio of animal manure and water used was 1:1 in 12 days of Hydraulic Retention Time (HRT). The produced gas was measured by the volumetric water replacement method. In the first phase, the best pH was chosen in the experimental test with different pH ranges. Three set-ups were prepared with different pHs (6.5, 7, 7.5). The results showed that the pH had significant effects on biogas yield, where pH 7 had the highest biogas production and pH 6.5 had the lowest. In the second phase, the effect of insulation of digester on the biogas yield of cow, sheep, and poultry manure was investigated. The experiments showed that the biogas produced from an insulated digester was higher than the transparent digester. Therefore, it is assumed that the study, which gives a maximum yield of biogas production from the batch digestion process, might meet future energy demand.
References
International Energy Agency, Energy and Climate Change. World Energy Outlook Special Report, OECD/IEA, Paris, 2015.
United Nations Environment Programme, The Emissions Gap Report. A UNEP Synthesis Report, UNEP, Nairobi, 2014.
Charles W, Barbara G. Biotechnology for production of fuels, chemicals and materials from biomass, Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology. 1993; 39: 41–59.
Mata-alvarez J, Mace S, Llabres P. Anaerobic digestion of organic solid wastes – an overview of research achievements and perspectives, Bioresource Technology. 2000; 74: 3–16.
FAO. World Livestock: Transforming the Livestock Sector through the Sustainable Development Goals; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2018.
Meat Atlas Facts and Facts and figures about the animals we Eat. Berlin, Germany; Heinrich Böll Foundation and Friends of the Earth Europe: Brussels, Belgium, 2014.
Ogbuewu P, Odoemenam U, Obikaonu O, Opara N, Emenalom O, Uchegbu C, Okoli C, Esonu O, Iloeje U. The growing importance of neem (Azadirachta indica A. Juss) in agriculture, industry, medicine and environment: A review. Research Journal of Medicinal Plant. 2011; 5(3): 230–245.
Chadwick D, Sommer S, Thorman R, Fangueiro D, Cardenas L, Amon B, Misselbrook T. Manure management: Implications for greenhouse gas emissions. Animal Feed Science Technology. 2011; 166–167: 514–531.
Webb J, Sommer G, Kupper T, Groenestein K, Hutchings J, Eurich-Menden B, Rodhe L, Misselbrook H, Amon B. Emissions of ammonia, nitrous oxide and methane during the management of solid manures. Agroecology and Strategies for Climate Change. 2012; 8: 67–107.
Nielsen B, Mladenovska Z, Westermann P, Ahring K. Comparison of two-stage thermophilic (68 °C/55 °C) anaerobic digestion with one-stage thermophilic (55 °C) digestion of cattle manure. Biotechnology Bioengineering. 2004; 86(3):291–300.
Tallou A, Haouas A, Jamali Y, Atif K, Amir S, Aziz F. Review on cow manure as renewable energy. In Smart Village Technology: Concepts and Developments; Patnaik S, Sen S, Mahmoud M.S, Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland. 2020; 17: 341–352.
Kaparaju P, Rintala J. Effects of temperature on post-methanation of digested dairy cow manure in a farm-scale biogas production system. Environmental Technology. 2003; 24: 1315- 1321.
Vindis P, Mursec B, Janzekovic M, Cus F. The impact of mesophilic and thermophilic anaerobic digestion on biogas production. Journal of Achievements in Materials and Manufacturing Engineering. 2009; 36 (2): 192-198
Orrico J, Orrico A, Lucas J, Sampaio A, Fernandes A, Oliveira E. Biodigestão anaeróbia dos dejetos da bovinocultuta de corte: influência do período, do genótipo e da dieta. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia. 2012; 41 (6): 1533-1538.
Barros R, Tiago F, Nascimento Y, Gushiken E, Calheiros H, Silva F, Stano J.Estudo da produção de biogás da digestão anaeróbia de esterco bovino em um biodigestor. Revista Brasileira de Energia. 2009; 15: 34-38.
Weber R. Produção de biogás com relação ao teor de sólidos voláteis dos dejetos de bovinocultura de leite. Revista Brasileira de Energias Renováveis. 2014; 3 (1):43-55.
Fatma A, Yuzaburo N, Maria K, Naomichi N, Yutaka N. Enhancement of methane production from co-digestion of chicken manure with agricultural wastes. Bioresource Technology. 2014; 159: 80-87.
Cunsheng Z, Gang X, Liyu P, Haijia S, Tianwei T. The anaerobic co-digestion of food waste and cattle manure. Bioresource Technology. 2013; 129: 170–176.
Benali M. Utilization of Cow, Poultry and Sheep Manure for biogas Production: A Comparative Analysis, Master’s thesis, Faculty of Engineering, Omar Al-Mukhtar University, Libya, 2o2o.
Benali M. Experimental Investigation of Biogas Production from Cow Dung in an Anaerobic Batch Digester at Mesophilic Conditions. Iranian (Iranica) Journal of Energy & Environment. 2019;10 (2):121-125.
Jayaraj S, Deepanraj B, Sivasubramanian V. Study on the effect of ph on biogas production from food waste by anaerobic digestion. The 9th international green energy conference. 2014; 799-805.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Muetaz Mohammed, Ahmad Belkair, Tarek Hamad, Abraheem Jirhiman, Razena Hassan, Ali Ahmeedah

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.





